16+ Plantar Foot Surface
Plantar fasciitis PF is characterized by pain on weight-bearing in the medial plantar area of the heel metatarsalgia MTG by pain on the plantar surface of the forefoot radiating into the toes. The PubMed Embase and Scopus databases were queried for published articles.

Mbt Plantar Fasciitis Plantar Fasciitis Treatment David Redfern
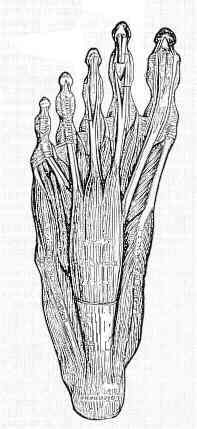
The nerves and vessels of the plantar foot traverse the fascial plane just deep to the first muscle layer.
. Click the card to flip. Familiarity with the normal anatomy of the plantar tendons and its appearance at magnetic resonance MR imaging and ultrasonography US is essential for recognizing plantar tendon disorders. A systematic literature search was performed to identify articles relating to reconstruction of the plantar skin and soft tissue.
Plantar Surface of Foot. Web Follow the nerve and vessels forward into the foot. The posterior tibial vessels divide into medial and lateral plantar vessels.
Their muscle bellies form the surface of the lateral foot sole ball of the little toe. It is covered with hairless usually nonpigmented skin that is especially thickened and provided with epidermal ridges over the weight-bearing areas. Common causes of foot pain include plantar fasciitis bunions flat feet heel spurs mallet toe metatarsalgia claw toe and Mortons neuroma.
Web The lower calcaneal surface or plantar surface forms from the forward protrusion of the calcaneal tuberosity which leads to the formation of medial and lateral processes on both sides and the calcaneal tubercle in the front. 16 Plantar Surface of Foot Flashcards Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Flexor Digitorum Brevis Origin Flexor Digitorum Brevis Insertion Flexor Digitorum Brevis Innervation and more. Structure Deep anatomy of the sole The glabrous skin on the sole of the foot lacks the hair and pigmentation found elsewhere on the body and it has a high concentration of sweat pores.
Planta pedis TA plantar region regio plantaris plantar surface of foot. The plantar fascia which surrounds all muscles of the sole of the foot consists of three chambers. Web The lateral chamber formed by the plantar fascia contains three muscles.
The articulation or joints are invested by joint capsules and ligaments which lend stability to the joints. The following muscles lie within the lateral compartment. This tissue originates deep within the plantar surface of the calcaneus heel bone and covers the distance to the base of each of the five toes.
Web The plantar fascia is not a nerve tendon or muscle but rather a strong fibrous tissue Figure 16. When the foot rolls off the ground during walking the toes dorsiflex and pull on the plantar fascia. Web Anatomy and supply Central plantar muscles The central muscles of the foot sole lie within the central compartment between the muscles of the big and little toe.
Reliable figures on lifetime prevalence in Germany are lacking. Web A comprehensive literature review is presented to better define available reconstructive options for resurfacing the plantar foot. Flexor digitorum brevis FDB abductor digiti minimi.
Web Tendon disorders along the plantar aspect of the foot may lead to significant symptoms but are often clinically misdiagnosed. In this article we present the clinical findings of the diseases that most commonly cause plantar pain the diagnostic procedures available and an overview of the treatment options. Extrinsic Muscles of the Foot Peroneus Longus.
Together they form the central surface of the foot sole. While the cause is not well understood there is believed to be a genetic component to the disorder. The muscles lying within the medial group form a bulge referred to as the ball of the big toe.
Web The 7-foot-3 Porzingis was traded to the Celtics this offseason and agreed to a two-year 60 million extension that will tie him to Boston through the 2025-26 season at a total of 96 million. The compartment comprises numerous short foot muscles in different layers. The tibial nerve divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves.
The muscles are attached to the osseous structures via tendons. Web Anatomy and supply. Also there are 29 muscles responsible for the movement of the osseous structures of the foot and ankle.
They act collectively to stabilise the arches of the foot and individually to control movement of the digits. What are the 3 portions of the plantar aponeurosis. Web In humans the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect.
Web Medical Conditions Diagnosis Treatment The anatomy of the foot and its function can predispose to common foot problems. Lateral central and medial. Web The plantar surface was divided into eight anatomical regions including great toe T1 lesser toes T2-5 first metatarsal M1 central forefoot M23 lateral forefoot M45 midfoot MF.
They are all innervated by the lateral plantar nerve S1-S2 a branch of the tibial nerve. Web It presents as a painless lump on the medial border of the plantar surface of the foot. Web Pain on the plantar surface of the foot subsumes constellations of symptoms arising from various underlying conditions.
Web The articular surfaces of bones have a covering of articular cartilage. They are innervated by the medial or lateral plantar nerves which are branches of the tibial nerve. Web There are ten intrinsic muscles located in the plantar aspect sole of the foot.
Most superficial of all the layers. Click the card to flip. It contributes to the surface anatomy of the medial sole of the foot and is easy to palpate.
Clinical assessment and imaging with MRI or diagnostic ultrasound are used to make the diagnosis. Web This image shows the anatomy of the plantar foot and is labeled with corresponding identification tags. Web Mechanical stress such as plantar pressure and shear stress is higher in these two areas than in other areas of the foot 4 and this stress is associated with the development of skin ulcers in.
The lateral calcaneal surface is a wide flat surface except for the two bony protrusions on it. Web the inferior aspect or bottom of the foot much of which is in contact with the ground when standing. Web The intrinsic muscles of the foot are further divided into dorsal and plantar groups and there are four layers of the plantar muscles.

Foot Dysfunctions Plantar Fasciitis And Pes Planus And Cavus Flashcards Quizlet

Plantar Area An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Plantar Division The Plantar Surface Was Divided Into Eight Anatomical Download Scientific Diagram

Heel And Arch Pain Plantar Fascitis No One Size Fits All Approach Part 1 The Body Works Clinic

Plantar Surface Of Foot Flashcards Quizlet

Foot Structures Of The Plantar Surface

Foot Plantar Surface Deepest Human Body Help

Pain On The Plantar Surface Of The Foot 08 02 2019

Plantar Surface Vet Anatomy Imaios

Foot Plantar Surface Deepest Human Body Help

Plantar Fasciitis That Constant Foot Pain What Never Seems To Go Away

Florida Raceplace Magazine March April 2023 By Florida Raceplace Magazine Issuu
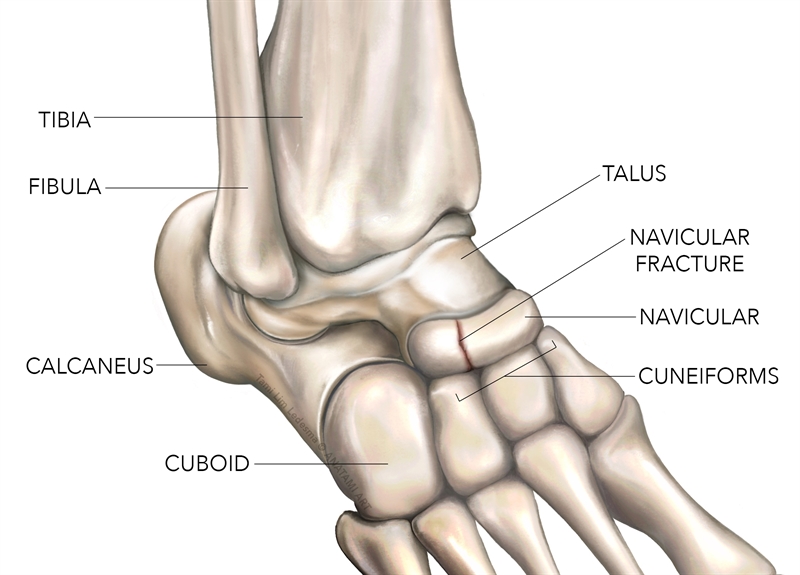
Sports Injury Bulletin Anatomy Navicular Stress Fracture A High Impact Risk For Young Athletes

Plantar Fascia Wikipedia

Foot Plantar Surface Superficial Dissection On The Dorsum Lower Limb Anatomy Series 1 0 3d Anatomy Series Shop Erler Zimmer
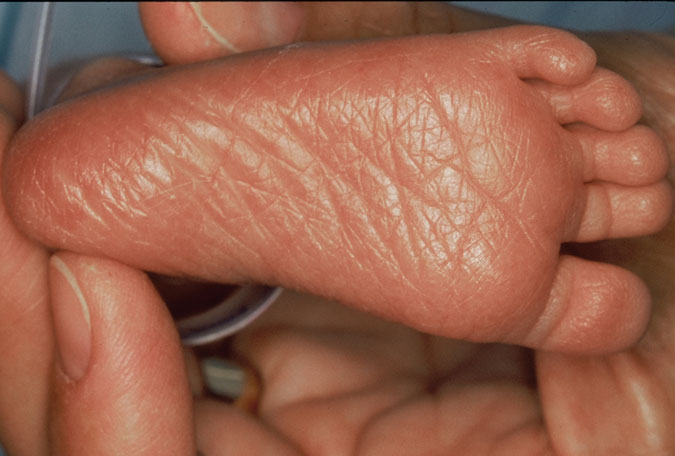
Ballard Score Training 3 Plantar Surface Ballard Score

Amazon Com Soleaid Xt Ii Performance Insoles Medium Flex Arch Support With Dual Density Shock Absorbing Foam Orthotic Shoe Inserts For Athletic And Daily Life On Your Feet Men 11 11 5 Women